Investigators link Salmonella outbreak to fresh organic basil from Trader Joe’s

Fresh organic basil sold at Trader Joe’s stores is behind a multi-state outbreak of Salmonella Typhimurium infections.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is investigating the outbreak with the Food and Drug Administration. As of this afternoon, a dozen people across seven states have been confirmed with the outbreak strain of Salmonella.
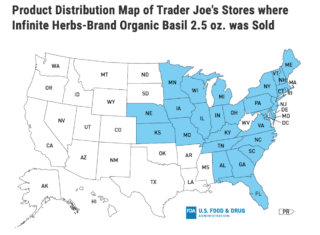
The implicated fresh basil is sold in 2.5-ounce clamshell packaging under the Infinite Herbs brand. It was distributed to Trader Joe’s stores in Alabama, Connecticut, Washington D.C., Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Massachusetts, Maine, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, North Carolina, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, Vermont and Wisconsin.
Public health officials are interviewing patients and found that seven of eight patients interviewed reported exposure to fresh organic basil from Trader Joe’s stores before becoming ill.
Traceback data collected by the FDA determined that Infinite Herbs LLC, in Miami, FL, was the supplier of the 2.5-ounce packages of organic basil sold at Trader Joe’s stores.
Trader Joe’s has voluntarily removed all Infinite Herbs brand organic basil packed in 2.5-ounce clamshell packaging from their stores, and this product should no longer be available for sale.
The outbreak investigation is ongoing to determine the source of contamination and whether additional products are linked to illnesses.
About Salmonella infections
Food contaminated with Salmonella bacteria does not usually look, smell, or taste spoiled. Anyone can become sick with a Salmonella infection. Infants, children, seniors, and people with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of serious illness because their immune systems are fragile, according to the CDC.
Anyone who has eaten any fresh organic basil from Trader Joe’s stores and developed symptoms of Salmonella infection should seek medical attention. Sick people should tell their doctors about the possible exposure to Salmonella bacteria because special tests are necessary to diagnose salmonellosis. Salmonella infection symptoms can mimic other illnesses, frequently leading to misdiagnosis.
Symptoms of Salmonella infection can include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever within 12 to 72 hours after eating contaminated food. Otherwise, healthy adults are usually sick for four to seven days. In some cases, however, diarrhea may be so severe that patients require hospitalization.
Older adults, children, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems, such as cancer patients, are more likely to develop severe illness and serious, sometimes life-threatening conditions.
Some people get infected without getting sick or showing any symptoms. However, they may still spread the infections to others.
(To sign up for a free subscription to Food Safety News,click here)




